Article publié par Aadil Yunush, Data Scientist chez Keyrus
Sequence Modelling is an unsupervised technic that enables to get the probability of a sequence of states given an initial state in which the agent is. Sequence data can be seen in multiple fields of machine learning such as webpage visits, credit scoring, stock prices, shopping cart analysis, or text sequence prediction. Markov Model, named after the Russian mathematician Andrey Markov is a stochastic model that aim to sequence modelling. The details of algorithms used to train models are beyond the scope of this article but you will find a very good description in links given at the end of this article. Trough out this article I will make a link between Markov Model and hidden Markov Model and try to show how Markov models could be used in a more general data science problematic.
Sequence Modelling with Markov Model
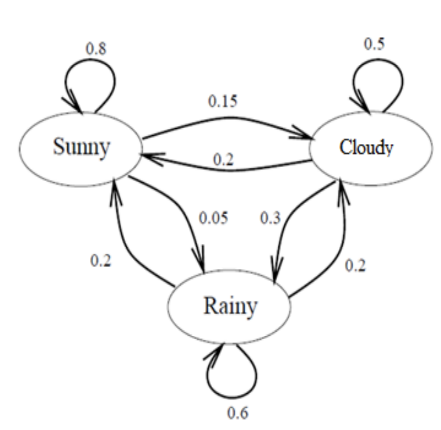
As you may know, a Markov model is a stochastic sequence modelling method that satisfy the Markov property which says that future state depends only on the present state. To illustrate this let’s use the classic weather use case. We have 3 states, s1(sunny), s2 (cloudy) and s3(rainy) and this property says that at time t (suppose t is an integer):
P(weather(t) / weather(t’ < t)) = P(weather(t) / weather(t-1))
Thus, we will have for a sequence s1,s2,s3 the following simplification for the joint probability:
P(s3 ,s2,s1) = P(s3/s2,s1)P(s2,s1) = P(s3/s2,s1)P(s2/s1) P(s1) = P(s3/s2)P(s2/s1) P(s1)
Although Markov property suggest an exclusive dependence to the immediate previous state, we can find a second order Markov model or third order Markov Model thus we will have P(s(t)/s(t-1),s(t-2)) for the second order for example.
In this example, we can modelize this graph using a single 3x3 matrix containing conditional probabilities, let A be a matrix of size n*m with A(i,j) = p( s(t)=j / s(t-1)=i). We can notice that for each i in 1 to n, A(i, :) equals to 1. Moreover, we need to start randomly at a state, this information will be contained in vector π of size 1*n. If we consider the sequence S = (sunny,cloudy,rainy,cloudy),
P(S) = P(cloudy/rainy)*P(rainy/cloudy)*P(cloudy/sunny)*P(sunny), generalizing this to a sequence of length L , s(0),…,s(L), we will have which we can rewrite in:
P(S) = π *AL , also we can notice that the previous form is computationally cheaper when the length of the sequence become too long.
Sequence Modelling using Hidden Markov Model

We often heard about hidden Markov model asking in what they differ from Markov model. In fact, this consist in having one or more hidden layers of unobserved features. Moving from the weather example we would have this new graph, previous variables becoming unobserved:
Let say we have our vector π and our matrix A, we need another matrix B with B(j,k) being the probability of observing variable k from hidden state j. We will call O the sequence of observed variables thus our HMM will be characterized with λ = (π,A,B). There are three problems often encountered in Markov models: how to find P(O/ λ) given λ, how do we choose sequence S to maximize P(O,S/ λ), the joint probability of the observation and the state sequence and how do we adjust λ so that P(O/ λ) or P(O,S/ λ) is maximized. The first problem can be resolved using the forward and backward procedure, the second one with the Viterbi algorithm and the third one with the Baum-Welch Formula. This algorithm as said earlier are beyond the scope of this article but the hard part is to understand to what extend your data science problematic can be modelized by a Markov process and to define what are the ensemble of sequences you may have and dress the parameter λ definition.
An Industrial Problem: Prediction of the Life Time Value
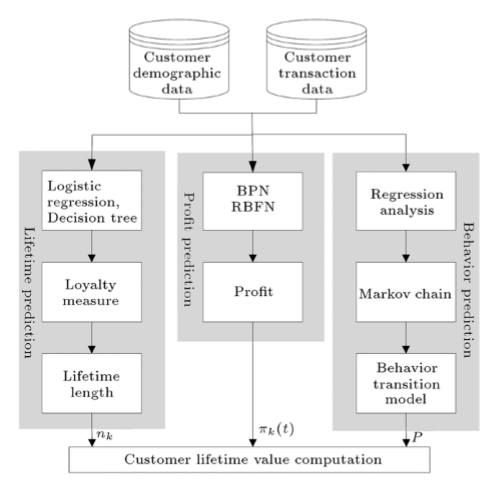
A paper of Sharif University of Technology illustrates well how sequence modelling could be a part of an industry problematic such as finding the life time value of a customer of an auto repair and maintenance company in Taiwan.
In their work, they find that LTVk , the life time value for the kst customer is equal to CVk + FVk , the current value of the customer and the future value of this latter. Current value is easily calculated with formula and future value is harder to compute and it is defined as
where nk is the lifetime length, Ik is the initial state vector of the kth customer, P the state transition probability matrix and πk(t) is a vector of profits generated by the kth customer under all possible states at time t.
A supervised method enables to get the churn probability that will enable to measure the churn period or lifetime length noted y which will follow a geometric distribution. This will give the following probability of lifetime length and the corresponding expected value . Furthemore, a data exploration underline the fact that a few customers visit more than 4 times a year thus for a given year we can have following sequence S = [0,1,2,3,4] so P will be a 5*5 matrix. Assuming the number of times the customer visit the company follows a Poisson distribution, the probability of visiting x times will be .
Parameters λi could be estimated as a weighted average of the number of visits per year per customers. This example is really interesting to show how a Markov process could be a part of a more global data science problem. Hidden Markov Model can also be a part of a wide range of computing intelligence process such as speech recognition or reinforcement learning. Don’t hesitate to read the two following sources that inspired me to write this article that will for sure give you a complete insight of the points I have written about.
Sources “Customer lifetime value prediction by a Markov chain based data mining model: An application to an auto repair and maintenance company in Taiwan” C-j. Cheng, S.W.Chiu, J-Y. Wu (Sharif University of Technology) “A Tutorial on Hidden Markov Models” Rakesh Dugad, U.B. Desai (Indian Institute of Technology)